cyxCoder
明天你会感谢今天奋力拼搏的你。
ヾ(o◕∀◕)ノヾ
AI大模型系列:(四)结构化输出
一、概念介绍
结构化输出(Structed Outputs)是指让 LLM 输出符合机器可解析的格式,典型的是 JSON 结构。有三条技术路径:
- JSON mode
- Function Calling
- JSON Schema
JSON mode在提示工程的文章中已经有涉及,其实就是response_format字段的传值,json_object就代表的JSON mode。
本文主要讲解Function Calling的机制,然后介绍一下一个新的方式:JSON schema
二、ChatGPT的Actions
了解Function Calling之前先来说说ChatGPT的Actions,其内置在GPTs中,解决了落地场景问题,但没能成功商业化。
Actions的官方文档:https://platform.openai.com/docs/actions
Actions工作流程:
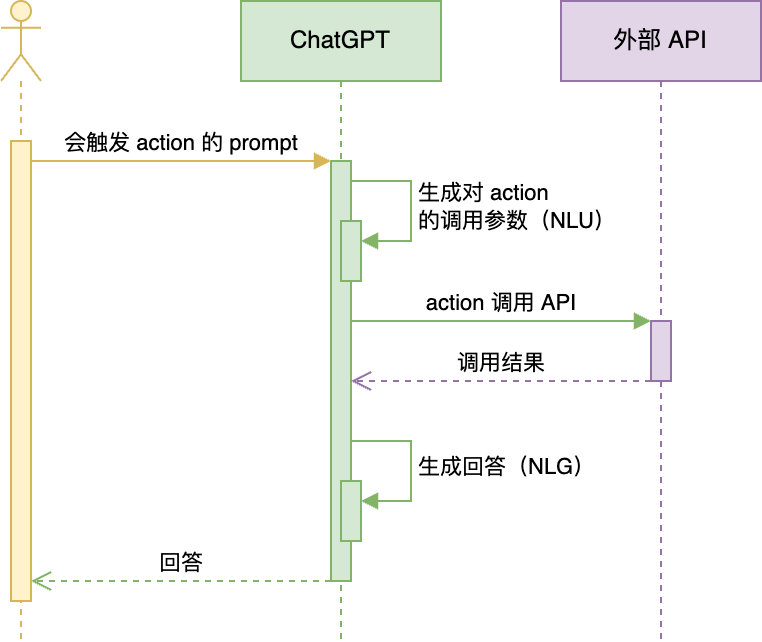
- 通过 Actions 的 schema,GPT 能读懂各个 API 能做什么、怎么调用(相当于人读 API 文档)
- 拿到 prompt,GPT 分析出是否要调用 API 才能解决问题(相当于人读需求)
- 如果要调用 API,生成调用参数(相当于人编写调用代码)
- ChatGPT(注意,不是 GPT)调用 API(相当于人运行程序)
- API 返回结果,GPT 读懂结果,整合到回答中(相当于人整理结果,输出结论)
三、Function Calling的机制
相对于Actions,Function Calling的原理差不多,只是Function Calling是生成函数的调用参数,具体的函数调用由你自己去完成,最后把结果返回给AI,AI再生成回答结果。

示例:
在此只是调用了一个内置的sun方法进行示例,其实参数tools的数据结构为一个数组,可以传入多个funcution供其选择,其返回的函数调用也可能会有多个。也可以自定义Function,其中的逻辑可以发挥你的想象,去调用 API或者查询数据库各种方式实现。
# 初始化
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
import json
from math import *
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
client = OpenAI()
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-4o-mini"):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
temperature=0.7,
tools=[{ # 用 JSON 描述函数。可以定义多个。由大模型决定调用谁。也可能都不调用
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "sum",
"description": "加法器,计算一组数的和",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"numbers": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "number"
}
}
}
}
}
}],
)
return response.choices[0].message
prompt = "Tell me the sum of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10."
# prompt = "桌上有 2 个苹果,四个桃子和 3 本书,还有 3 个番茄,以及三个傻瓜,一共有几个水果?" # 能识别出中文数字,傻瓜不是水果
# prompt = "1+2+3...+99+100"
# prompt = "1024 乘以 1024 是多少?" # Tools 里没有定义乘法,可能AI会自己算出来,也可能会一本正经的胡说八道。
# prompt = "太阳从哪边升起?" # 不需要算加法,则不会要求调用sun函数
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个数学家"},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
response = get_completion(messages)
# 把大模型的回复加入到对话历史中。必须有
messages.append(response)
# 如果返回的是函数调用结果,则打印出来
if (response.tool_calls is not None):
# 是否要调用 sum
tool_call = response.tool_calls[0]
if (tool_call.function.name == "sum"):
# 调用 sum
args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
result = sum(args["numbers"])
# 把函数调用结果加入到对话历史中
messages.append(
{
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id, # 用于标识函数调用的 ID
"role": "tool",
"name": "sum",
"content": str(result) # 数值 result 必须转成字符串
}
)
# 再次调用大模型
response = get_completion(messages)
messages.append(response)
print("=====最终 GPT 回复=====")
print(response.content)
def print_json(data):
"""
打印参数。如果参数是有结构的(如字典或列表),则以格式化的 JSON 形式打印;
否则,直接打印该值。
"""
if hasattr(data, 'model_dump_json'):
data = json.loads(data.model_dump_json())
if (isinstance(data, (list))):
for item in data:
print_json(item)
elif (isinstance(data, (dict))):
print(json.dumps(
data,
indent=4,
ensure_ascii=False
))
else:
print(data)
print("=====对话历史=====")
# 格式化打印输出一下对话记录
print_json(messages)返回结果:
=====最终 GPT 回复=====
The sum of the numbers from 1 to 10 is 55.
=====对话历史=====
{
"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个数学家"
}
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Tell me the sum of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10."
}
{
"content": null,
"refusal": null,
"role": "assistant",
"audio": null,
"function_call": null,
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_rKvXvZBzpD0Myq7TUWuTa68C",
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"numbers\":[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]}",
"name": "sum"
},
"type": "function"
}
]
}
{
"tool_call_id": "call_rKvXvZBzpD0Myq7TUWuTa68C",
"role": "tool",
"name": "sum",
"content": "55"
}
{
"content": "The sum of the numbers from 1 to 10 is 55.",
"refusal": null,
"role": "assistant",
"audio": null,
"function_call": null,
"tool_calls": null
}注意:
- 函数声明是消耗 token 的。要在功能覆盖、省钱、节约上下文窗口之间找到最佳平衡
- Function Calling 不仅可以调用读函数,也能调用写函数。但官方强烈建议,在写之前,一定要有真人做确认。
四、通过JSON schema控制回复格式
这是 OpenAI 2024 年 8 月 6 日发布的新 API,但目前未见国产大模型跟进。以后很可能又成为一个标准,因为其比 JSON mode 更稳定,更容易控制。
理解起来其实很简单,就是定义一个类,放入请求参数的response_format字段里,以此作为AI返回结果的JSON格式。
注意记得把openai更新到最新版本,低版本可能没有此方式:
pip install --upgrade openai示例:
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
from pydantic import BaseModel
from openai import OpenAI
# 加载 .env 文件中定义的环境变量
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
client = OpenAI()
class CalendarEvent(BaseModel):
name: str
date: str
address: str
participants: list[str]
completion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse( # 使用 beta 接口
model="gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18", # 必须是版本大于 gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 或 gpt-4o-2024-08-06 的模型
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "解析出事件信息。"},
{"role": "user", "content": "一般我会于周一晚上,在家中与妻子孩子一起玩游戏。"},
],
response_format=CalendarEvent,
)
event = completion.choices[0].message.parsed
print(type(event))
print(event)结果显示:
<class '__main__.CalendarEvent'>
name='家庭游戏时间' date='每周一晚上' address='家中' participants=['我', '妻子', '孩子']实际请求的报文结构:
{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "解析出事件信息。"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "一般我会于周一晚上,在家中与妻子孩子一起玩游戏。"
}
],
"response_format": {
"type": "json_schema",
"json_schema": {
"name": "calendar_event",
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": { "type": "string" },
"date": { "type": "string" },
"address": { "type": "string" },
"participants": {
"type": "array",
"items": { "type": "string" }
},
"required": ["name", "date", "address", "participants"],
"additionalProperties": false
}
},
"strict": true
}
}
}五、附录
内容引自孙志岗老师的AI 大模型系列课程:https://agiclass.ai/
全部评论